오버로딩(Overloading)
: 매개변수의 개수와 타입은 다르지만 이름이 같은 메서드를 여러 개 정의하는 것
컴퓨터가 함수를 구분하는 시그니처
1. 함수명
2. 함수의 매개변수의 개수
3. 함수의 매개변수의 타입
-> 오버로딩의 경우 함수명이 같으므로
함수의 매개변수의 개수와 타입을 달리하는 것
즉 오버로딩이란,
메서드 중복정의
일반적으로 메서드 사용 시 메서드명을 구분해서 사용
하지만 같은 기능을 가지고 있는 메서드라면 매번 이름을 정의하는 것이 불필요하다
ex1.
정수형 값을 두 개 전달받아 두 수의 합을 출력하는 메서드 구현
public class sumEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum (10, 20);
sum (1.23, 3.12);
}
static void sum (int x, int y) {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
static void sum (double x, double y) {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
}
동일한 메서드인데 숫자 타입에 따라 다를 경우
-> 이 경우 x와 y의 값이 int인 경우 int 값 메서드를 사용하고
double인 경우 double값 메서드를 사용해 값을 출력한다
ex2.
public class sumEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum (10, 20);
sum (1.23, 3.12);
sum (10, 20, 30);
}
//메서드의 매개변수 타입의 변화
static void sum (int x, int y) {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
static void sum (double x, double y) {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
// 메서드의 개수가 다른 경우
static void sum (int x, int y, int z) {
System.out.println(x+y+z);
}
}
ex3.
// 두 수를 전달받아 사칙연산 구현하기
// 단, 정수와 실수 모두 가능해야 한다
public class Calc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
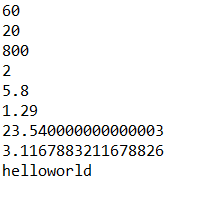
System.out.println(sum (40, 20));
System.out.println(sub (40, 20));
System.out.println(mul (40, 20));
System.out.println(div (40, 20));
System.out.println(sum (1.3, 4.5));
System.out.println(sub (3.54, 2.25));
System.out.println(mul (5.5, 4.28));
System.out.println(div (8.54, 2.74));
System.out.println(sum ("hello", "world"));
}
// 정수형의 사칙연산
static int sum (int x, int y) {
return x+y;
}
static int sub (int x, int y) {
return x-y;
}
static int mul (int x, int y) {
return x*y;
}
static int div (int x, int y) {
return x/y;
}
// 실수형의 사칙연산
static double sum (double x, double y) {
return x+y;
}
static double sub (double x, double y) {
return x-y;
}
static double mul (double x, double y) {
return x*y;
}
static double div (double x, double y) {
return x/y;
}
// 문자열의 덧셈연산
static String sum (String x, String y) {
return x+y;
}
}
JAVA Eclipse 01 프로그램, 프로그래밍, 기계어, JAVA
https://developernew.tistory.com/63
JAVA Eclipse 02 자바 출력메서드와 입력메서드
https://developernew.tistory.com/71
JAVA Eclipse 03 변수, 자료형, 형변환, 변수의 상수화
https://developernew.tistory.com/74
JAVA Eclipse 04 연산자 정의, 연산자 종류, 연산자 우선순위
https://developernew.tistory.com/78
JAVA Eclipse 05 논리연산자, 비트연산자
https://developernew.tistory.com/80
JAVA Eclipse 06 기타연산자 - 삼항연산자, 대입연산자, 복합대입연산자, instanceof
https://developernew.tistory.com/84
JAVA Eclipse 07 제어문 : 조건문
https://developernew.tistory.com/88
JAVA Eclipse 08 제어문 : 조건문 switch + Random 클래스
https://developernew.tistory.com/93
JAVA Eclipse 09 제어문 : 반복문 for
https://developernew.tistory.com/102
JAVA Eclipse 10 제어문 : 반복문 while, do-while
https://developernew.tistory.com/103
JAVA Eclipse 11 제어문 : 반복문의 break, continue
https://developernew.tistory.com/106
JAVA Eclipse 12 배열 : 배열의 개념 및 사용
https://developernew.tistory.com/107
JAVA Eclipse 13 배열 : 예제풀이, 로또번호 생성기
https://developernew.tistory.com/115
JAVA Eclipse 14 배열 : 다차원배열
https://developernew.tistory.com/117
JAVA Eclipse 15 배열의 복제, for ~ each문
https://developernew.tistory.com/120
JAVA Eclipse 16 카페 주문 시스템(키오스크) 배열과 제어문(반복문, 조건문)으로 풀기https://developernew.tistory.com/124
'Backend > JAVA2 멘토시리즈' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JAVA Eclipse 20 클래스와 객체 (0) | 2023.05.07 |
|---|---|
| JAVA Eclipse 19 객체지향 언어 (0) | 2023.04.10 |
| JAVA Eclipse 17 method 메서드(메소드) (0) | 2023.04.07 |
| JAVA Eclipse 16 카페 주문 시스템(키오스크) 배열과 제어문(반복문, 조건문)으로 풀기 (0) | 2023.04.06 |
| JAVA Eclipse 15 배열의 복제, for ~ each문 (0) | 2023.04.05 |